Ethereum’s security model has long been admired for its resilience, but as the ecosystem scales, the need to maximize validator incentives and network robustness is more pressing than ever. EigenLayer restaking has emerged as a pivotal innovation, allowing Ethereum validators to amplify the utility of their staked ETH while enhancing security for both themselves and emerging protocols. This technical guide explores how restaking works under the hood and why it is redefining the landscape for validator security.
The Restaking Paradigm: Multiplying Security Without Extra Capital
At its core, restaking enables Ethereum validators to extend their staked ETH’s protective reach beyond Ethereum’s consensus layer. Through EigenLayer, this same capital acts as collateral safeguarding additional protocols, known as Actively Validated Services (AVSs): without requiring new or separate deposits. This pooled security model means that each validator’s economic stake helps secure multiple services simultaneously, raising the bar for would-be attackers and reducing fragmentation across the ecosystem.
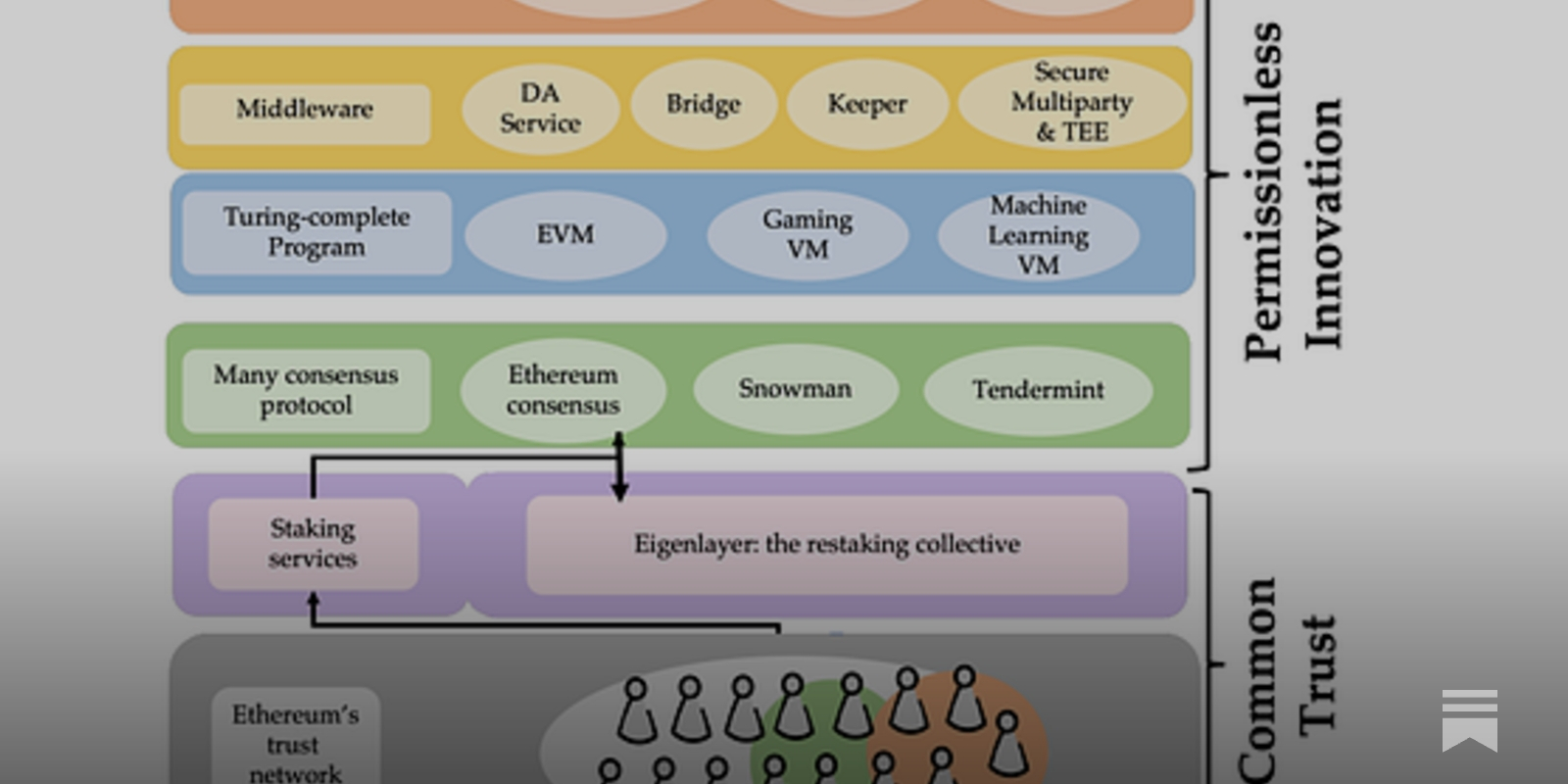
This approach is particularly attractive in today’s competitive DeFi environment, where new protocols often struggle to bootstrap their own validator sets. By tapping into Ethereum’s existing validator pool, AVSs inherit robust cryptoeconomic guarantees from day one. For validators, this translates into higher potential rewards and a more diversified risk profile, provided they navigate the technical nuances and risks responsibly.
Mechanics of Restaking: Liquid vs. Native Approaches
EigenLayer supports two primary forms of restaking:
- Liquid Restaking: Validators or delegators deposit Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) such as stETH, rETH, or cbETH into EigenLayer smart contracts. This method is highly accessible and allows a broader spectrum of participants to join the restaking process.
- Native Restaking: Here, validators link their staked ETH directly to EigenLayer by configuring withdrawal credentials to route through an EigenPod contract. This path requires operating a full validator node and is not constrained by LST mechanics or custodial risks.
The choice between liquid and native restaking depends on participants’ technical expertise, risk tolerance, and capital flexibility. Both models funnel cryptoeconomic security into EigenLayer’s architecture, but native restakers face stricter operational requirements and potentially greater exposure to slashing events.
Pooled Security and Slashing: Incentivizing Integrity at Scale
The heart of EigenLayer’s security enhancement lies in its unique slashing mechanism. By opting into restaking, validators consent to additional slashing conditions imposed by each AVS they support, on top of Ethereum’s base protocol rules. If a validator acts maliciously or fails to meet an AVS’s uptime or performance standards, their staked ETH (or LSTs) can be slashed proportionally.
This layered slashing framework creates powerful incentives for honest participation while deterring collusion or negligence across all supported services. Importantly, EigenLayer aggregates these risks across a shared pool of validators, making large-scale attacks prohibitively expensive and complex.
Pooled security doesn’t just protect individual AVSs, it strengthens Ethereum’s broader DeFi fabric by providing new projects with instant access to proven cryptoeconomic defenses. For an in-depth look at how these mechanisms are shaping decentralized finance, see our guide on the role of EigenLayer restaking in DeFi ecosystems.
The Governance Layer: Community Oversight and Risk Mitigation
No technical system is complete without robust governance. EigenLayer employs a community-driven approach where stakeholders can vote on slashing parameters, AVS onboarding, and other critical protocol settings. In addition, a dedicated veto committee reviews all slashing incidents, providing a crucial failsafe against false positives or malicious governance attacks.
This multi-tiered oversight helps maintain decentralization while ensuring that validator slashing remains fair, transparent, and aligned with long-term network health.
However, with increased reward opportunities come heightened risks. Validators must carefully assess the slashing conditions of each AVS before opting in. Because slashing can occur at both the Ethereum consensus layer and within any supported AVS, the cumulative risk exposure can be substantial. In extreme cases of malicious activity or repeated failures, validators could forfeit up to 100% of their restaked ETH. This reality underscores the importance of due diligence, evaluating AVS reputation, operational track records, and understanding the technical nuances of each slashing contract.
To help validators navigate these complexities, EigenLayer offers transparent documentation and governance participation, but the ultimate responsibility rests with individual operators. As the protocol matures, we expect to see more tooling and analytics emerge to support risk management and AVS selection, further professionalizing the validator landscape.
Validator Security in Practice: A New Era for Ethereum Staking
In practice, EigenLayer restaking is already reshaping how Ethereum validators approach network participation. By extending their staked ETH to secure multiple protocols, validators unlock higher yields and play a direct role in strengthening the entire DeFi ecosystem. This capital efficiency is especially valuable for smaller operators and new entrants who can now access diversified rewards without needing to split or reallocate their stake.
For new protocols, EigenLayer’s pooled security model drastically lowers bootstrapping costs. Instead of launching with a small, untested validator set vulnerable to attacks, AVSs can immediately tap into Ethereum’s mature validator base and cryptoeconomic security. This not only accelerates innovation but also ensures that emerging services meet high standards for reliability and trust from day one. For more on how EigenLayer helps new protocols launch securely, see our analysis on reducing bootstrapping costs for new Ethereum protocols.
Community governance remains a cornerstone of EigenLayer’s resilience. Through voting on AVS onboarding and slashing parameters, stakeholders collectively shape protocol evolution and risk profiles. The veto committee adds an extra layer of assurance, helping maintain fairness in slashing events and upholding trust in the system.
Key Takeaways for Validators
- Restaking increases capital efficiency by allowing staked ETH to secure multiple protocols simultaneously.
- Pooled security raises the cost for attackers and helps protect both established and emerging services.
- Layered slashing conditions demand careful risk assessment and ongoing diligence from validators.
- Community governance and the veto committee provide important safeguards against slashing errors or abuse.
EigenLayer restaking is not just a technical upgrade, it’s a paradigm shift in how Ethereum validator security is conceptualized and deployed. As adoption grows, expect to see continued innovation in risk management tools, AVS design, and governance frameworks that further enhance both rewards and security for all participants.






